Speech Intelligibility is usually expressed as a percentage of words, sentences or phonemes correctly identified by a listener. Speech intelligibility can be measured directly without the use of measurement equipment. A number of talkers will speak words or sentences and a number of listeners will indicate what they hear.
The speech to noise ratio in a number of frequency bands in the speech frequency range. This speech to noise ratio in every band is multiplied by a weighting factor. The weighted values for all bands are added. The Articulation Index is expressed in a single number from 0 to 1.
An AI greater than 0.7 is excellent, between 0.5 and 0.7 is good, between 0.3 and 0.5 is acceptable for some applications and less than 0.3 is generally unsatisfactory.
The most popular method of measuring intelligibility in the US is Alcons (Articulation Loss of Consonants). It expresses intelligibility as the percentage loss of consonants.
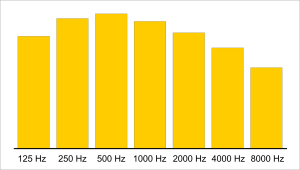
The measurement is calculated by 34% of the 2000 Hz range, 25% of the 1000 Hz range and 16% of the 500 Hz range.
0 percent Alcons would indicate perfect intelligibility with absolutely no loss of consonants. In sensitive environments a value of 5 percent should be reached, in regular spaces a value of up to 10 percent could be accepted. Anything more than 10 percent indicates bad intelligibility, 15 percent is the maximum loss acceptable.
 | |
 |  |
| speaker - room - mic - PA system - room - listener | measurement setup |
For STI testing, a test signal with speech-like characteristics is used. STI employs a complex amplitude modulation scheme to generate the test signal. The received signal in the measurement system is compared with the test signal concerning the depth of modulation in a number of frequency bands. Reductions in the modulation depth represent a loss of intelligibility. The Measurement of STI is defined by the standard IEC 60268 16:1998.
RASTI, Rapid Speech Transmission Index, is a more simplified version of STI.
A modulated test signal is fed to a loudspeaker at the talker's location. The receiver's microphone is positioned at the receiving listeners location. The system gives a direct read out of the measured RASTI value at the receiver position.
RASTI can also take account of the effects of reverberation, as well as background noise.
It tests in only two frequency bands, with the assumption that the response of the sound system is more than 100 Hz to 8 kHz or higher with a flat frequency response. Poor designed systems often tend to show a too optimistic measurement. Only for proper flat systems with the full frequency spectrum represent the measured values.
A RASTI value is in the range 0 to 1.
RASTI values above 0.75 is regarded as excellent, 0.6 to 0.75 as good, 0.45 to 0.6 as fair, 0.3 to 0.45 as poor, and below 0.3 as unsatisfactory.
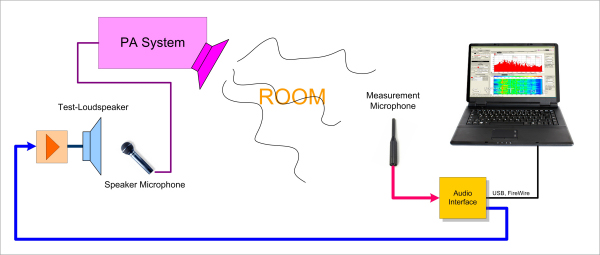 | |
| STI meaurement |
| STI versus % Alcons | ||||||
| STI | 0 - 0.3 | 0.3 - 0.45 | 0.45 - 0.6 | 0.60 - 0.75 | 0.75 - 1.0 | STI |
| inadmissible | poor | fair | good | excellent | ||
| ALcons | 100 - 33% | 33 - 15% | 15 - 7% | 7 - 3% | 3 - 0% | ALcons |